What is the neutral wire in electricity, and how to identify it?
In electricity, we all know the phase, an essential element used to carry voltage from one device to another. But there is also another element just as important that brings balance to any electrical circuit: the neutral wire. Discover today with DelightFire its utility, but also how to identify it.

Contents
Globally, what is the neutral wire used for?
Unlike the phase, which carries the electrical voltage of a device, the neutral serves as a reference point. The phase will have a variable electrical potential from one device to another. At the same time, the neutral wire will always remain with a zero electrical potential like a ground socket, i.e., at 0 Volt.
The neutral wires allow an installation to have two different voltages with only one transformer and one power cable. It is an essential element for your safety. It will also calculate your electricity bill at the electricity meter because it will be used to know how much you have consumed over a given period. Finally, the neutral wire allows the current used in your electrical installation to return to the electricity network to be redistributed afterward.
Where is the neutral wire located?
The neutral wire is found in the transformer. In the transformer, three low-voltage windings are connected in the form of a three-pointed star. Each winding has a common point with the other as well as three outputs, and it is this common point will correspond to the neutral wire that will be grounded on the transformer itself.
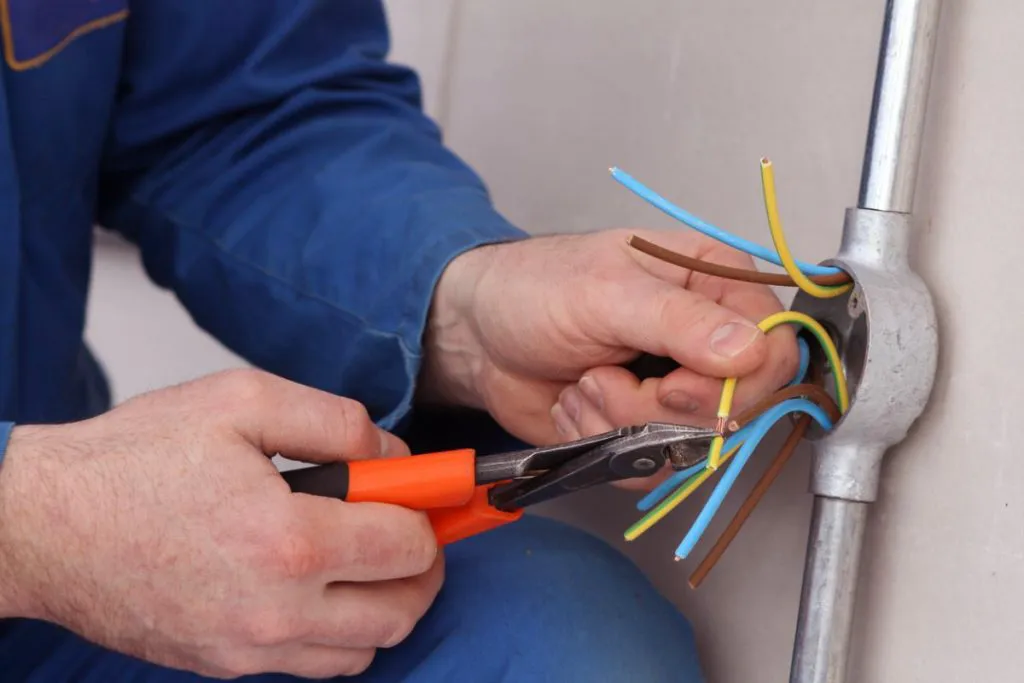
In a single-phase electrical installation, your installation will receive two electrical wires, one of the three phases and the neutral. This association makes your installation work safely when connected to an earth rod.
The different regimes of the neutral wires
It is important to know that the neutral wires are divided into three different regimes. These regimes vary according to the way the neutral is connected, but also according to the metal masses in relation to the earth.
Summary table of the different neutral systems
| System | 1st letter corresponding to the connection mode of the source neutral to earth | 2nd letter corresponding to the connection mode of the source metallic grounds to earth |
| TT system | The neutral is connected to earth on the transformer side (T). | The neutral is connected to earth on the user side (T) |
| IT system | The neutral is isolated on the transformer side (i) | The ground is connected to the user side (T) |
| TN system | Neutral is connected to the earth on the transformer side (T). | Earth is connected to the neutral on the user side (N) |
Easily identify the neutral wire by its color.
In an electrical installation, it is important to know that each electrical wire has a specific function, whether the phase, neutral or ground wire. To make it easier to identify the wires and to work safely, a color code has been established for each electrical cable purpose. We all know the red, black, or brown cables that correspond to the phase and the green/yellow cable that corresponds to the ground. The identification of the line for the neutral is also very simple to realize since it will be identified by a beautiful blue color which will thus completely denote the other colors of electrical cables.

